
Advanced Gum Disease Treatment &
Gingivitis Reversal Solutions
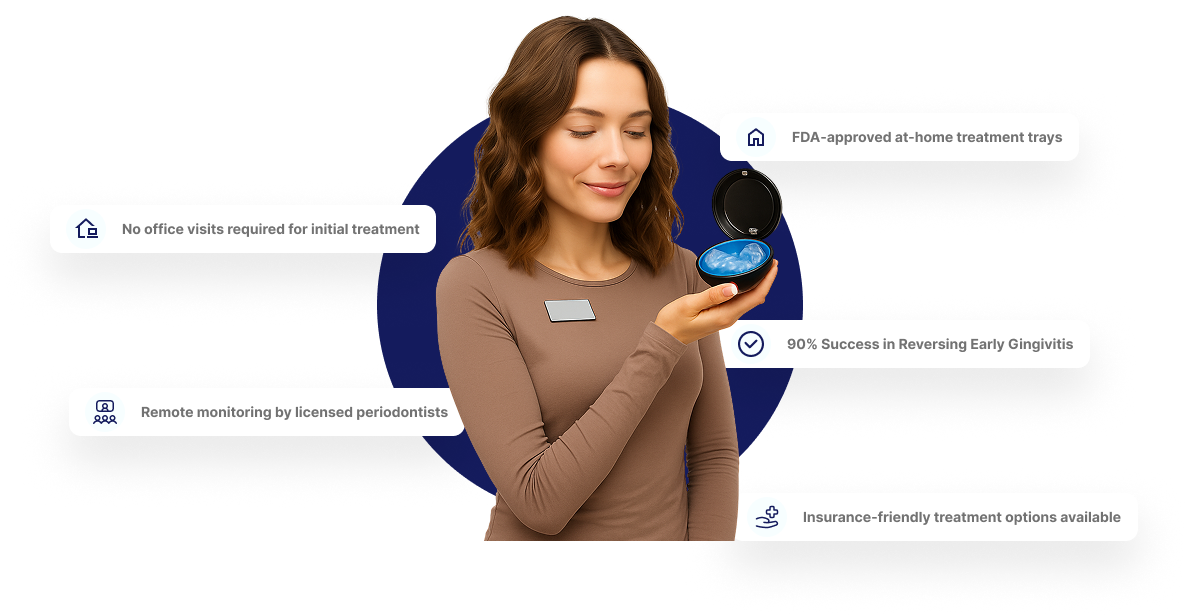
Reverse gum disease from home with Dentulu's proven treatment solutions. Our advanced periodontal therapy combines at-home gum disease reversal trays, remote monitoring technology, and expert dental supervision to heal gingivitis and prevent tooth loss. Over 47% of American adults suffer from gum disease - but effective treatment is now accessible, affordable, and convenient through our teledentistry platform.
Stage 1
Gingivitis (Reversible)
Red, swollen, bleeding gums
Bad breath that doesn't go away
Gum tenderness and sensitivity
Gingivitis is completely reversible with proper treatmentStage 2
Periodontitis (Manageable)
Gums pulling away from teeth (recession)
Deep pockets between teeth and gums
Loose or shifting teeth
Requires immediate professional interventionUnderstanding Gum Disease:
From Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection affecting your gums and supporting tooth structures. This progressive condition begins with gingivitis (gum inflammation) and can advance to periodontitis, potentially causing tooth loss and serious health complications.
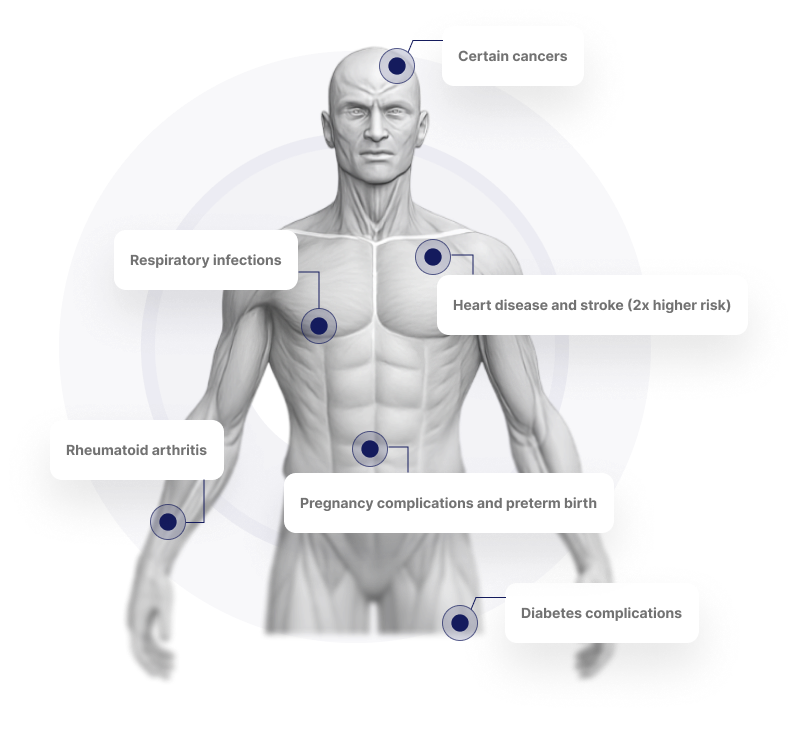
The Hidden Link Between Gum Disease &
Your Overall Health
Your oral health is closely connected to your overall well-being. Research shows that the bacteria responsible for gum disease don’t just stay in your mouth they can travel through the bloodstream, directly or indirectly contributing to serious health conditions throughout the body, including heart disease, diabetes complications, respiratory issues, and more
Dentulu's Revolutionary At-Home
Gum Disease Treatment
Dentulu combines custom-fitted treatment trays, remote monitoring, and advanced oral microbiome testing to deliver a powerful, personalized approach to gum disease care. With dentist oversight and AI-powered progress tracking, you’ll receive targeted therapy designed to stop infection, reduce inflammation, and restore gum health all from the comfort of home.
Prescription Gum Disease Reversal Trays
Dentulu’s custom-fit trays deliver prescription-strength antibacterial gels directly into infected gum pockets, providing round-the-clock healing that’s more effective than standard office treatments. Each tray is designed for maximum comfort and contact, with personalized protocols tailored to your disease severity. Safe for sensitive teeth and compatible with existing dental work, they offer a gentle yet powerful way to reverse gum disease at home under dentist supervision.
Custom Fit Trays
Maximum comfort & contact
Powerful Gels
Prescription-strength antimicrobials
Personalized Protocols
Based on disease severity
Gentle & Safe
Works with sensitive teeth and dental work
Weekly Check-Ins
Monitor gum health progress
Bacteria & Inflammation Tracking
Measure reduction and healing over time
Protocol Updates
Adjust treatment in real time for better results
Specialist Access
Ongoing guidance from periodontal experts
Remote Monitoring & AI-Powered Progress Tracking
With Dentulu, your treatment is never on autopilot. Advanced digital monitoring and AI insights track your gum health through weekly check-ins, measuring bacteria levels and inflammation reduction. Our periodontal specialists review your progress, adjust protocols in real time, and provide direct access for questions or support ensuring your care is always personalized and effective.
Comprehensive Oral Microbiome Analysis
Dentulu’s advanced OralDNA testing identifies the bacteria causing your gum disease, allowing specialists to create targeted treatment protocols. By understanding your unique oral microbiome, we address the root cause of gum disease for more effective, lasting results.
Start my OralDNA test today
Treatment Process
Simple, Effective, Convenient
Dentulu streamlines gum disease care into five easy steps. Start with a quick virtual consultation, then receive your at-home impression kit within days. Our lab crafts your custom trays and prepares your prescription, which are delivered to your door with virtual training and app setup. From there, weekly monitoring and real-time adjustments ensure your treatment is effective and tailored to your needs.
Start your gum disease reversalVirtual Consultation & Assessment (15 minutes)
- Complete health history review
- Digital gum disease evaluation
- Risk factor assessment
- Personalized treatment plan development
At-Home Impression Kit (Delivered in 2–3 days)
- Dentist-quality kits
- Detailed instructions with video guidance
- Prepaid shipping included
- 24/7 support available
Custom Treatment Tray Production (5–7 days)
- Lab-crafted for a perfect fit
- Prescription gels ready
- Tailored treatment plan
- Digital treatment timeline creation
Treatment Delivery & Initiation
- Delivered to your door
- Guided by a hygienist
- Ongoing progress tracking
- Emergency support contact information

Ongoing Monitoring & Adjustments
- Weekly progress check-ins
- Treatment effectiveness monitoring
- Protocol adjustments as needed
- Maintenance planning
Why Choose Dentulu for
Gum Disease Treatment?
Dentulu combines expert clinical care with modern technology to make gum disease treatment more effective, affordable, and accessible. From proven success rates and nationwide specialists to AI-powered monitoring and 24/7 support, every aspect of your treatment is designed for comfort, convenience, and lasting results.
Start my gum disease treatment todayClinical Excellence & Proven Results
High Success Rates
90% gingivitis reversal in 6–8 weeks, 85% periodontitis stabilization within 12 weeks, 95% patient satisfaction.
Expert Network
Board-certified periodontists and hygienists, 15+ years average clinical experience, trusted experts in advanced gum care.
Nationwide Care
Licensed in all 50 states, with ongoing education in advanced periodontal therapies.
Convenience & Accessibility Benefits
Save Time & Costs
No travel required, flexible schedules, and 60% savings compared to traditional therapy.
Smart Technology
Advanced AI-powered monitoring, real-time bacterial analysis, and secure HIPAA-compliant data.
Comprehensive Support
Reliable 24/7 emergency help, multilingual team assistance, and a full money-back guarantee.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for Every Stage
Dentulu treatments adapt to every stage of gum disease, from reversible early gingivitis to managing advanced periodontitis. Each option combines targeted therapies, expert clinical care, lifestyle tips, and AI-powered monitoring for effective, accessible, and lasting results.
Program
- Antibacterial therapy trays (4–6 weeks)
- Prescription rinses
- Sonic toothbrush
- Interdental tools
Expected Results
- 90% reversal (6–8 weeks)
- No bleeding
- Healthy pink gums
- Fresh breath
Moderate Periodontitis Management
Protocol
- Extended trays (8–12 weeks)
- Prescription antibiotics
- Advanced analysis/monitoring
- Nutritional support
Integration
- Local referrals
- Dentist coordination
- Pre-authorization
- Flexible plans
Advanced Periodontitis Support
Care Coordination
- Immediate specialist referral
- Collaborative plans
- Post-surgical support
- Long-term maintenance
Monitoring
- Quarterly digital assessments
- Bacterial culture
- Effectiveness tracking
- Preventive recommendations
Dentulu Prevention
Your Best Defense Against Gum Disease
Protect your gums with Dentulu’s prevention-focused care. Our approach combines daily oral hygiene, professional monitoring, and lifestyle support to stop gum disease from progressing.
Protect My Gums with DentuluDaily Oral Care Essentials
Follow a simple 4-step routine to keep your teeth strong and gums healthy brush, floss, rinse, and care for your gumline daily to prevent disease before it starts.
Brush
2 minutes with fluoride toothpaste
Floss
Remove plaque between teeth daily
Rinse
Antibacterial mouthwash
Eat for Gums
Clean along the gum line
Nutrition
Add Vitamin C, Omega-3s, and antioxidants to strengthen gums.
Stress Management
Reduce stress to support your body’s natural healing.
Hydration
Drink plenty of water to protect and cleanse your mouth.
Quit Smoking
Improve gum healing up to 3× faster.
Professional Preventive Care
Regular preventive visits help stop gum disease before it becomes serious. With routine cleanings, screenings, fluoride treatments, and custom nightguards, Dentulu ensures your gums and teeth stay protected long term.
Lifestyle Modifications for Healthy Gums
Healthy habits make a big difference in preventing and managing gum disease. A balanced diet, proper hydration, stress control, and quitting smoking all strengthen your gums and speed up healing especially when paired with regular dental checkups.
Cleanings 3–6 months
Remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Fluoride treatments
Extra protection for high-risk patients.
Quit Smoking
Improve gum healing up to 3× faster.
Custom nightguards
Guard against teeth grinding damage.
Get Your Free
Gum Disease Risk Assessment
In just 15 minutes, Dentulu can help you understand your gum health with a quick online questionnaire, secure photo uploads, and a virtual consultation with a periodontal specialist.
Start my free assessment nowComplete online health questionnaire
Upload photos using our secure app
Virtual consultation with periodontal specialist
Receive detailed treatment plan and pricing
Schedule treatment start date
What's Included in Your Assessment
Quick Links to Our Dental Solutions
Find what you need in seconds. Our quick links connect you directly to Dentulu’s most popular services and products, saving you time and keeping your smile care just a click away.
Testing & Diagnosis
Treatment Options
Monitoring
Support
Have questions?
Get answers
Gingivitis: 4-8 weeks for complete reversal
Mild Periodontitis: 8-16 weeks for stabilization
Advanced Periodontitis: Ongoing management with 3-6 month maintenance cycles